Titus’ work is divergent from traditional concepts of drawing in that the element of mask-making is central to his execution. Rather than creating sculptural paper masks, Titus instead uses the process and materials of drawing to engage the paper, resulting in a two-dimensional object with a compelling language of drawing - agile lines articulated in his distinct hand…
Read MoreHoliday Giving
Evelyn Reyes, Carrots (Green), 2006, oil pastel on paper, image courtesy Creativity Explored
If you participate in donating to important causes this holiday season, we extend our annual reminder to keep your local progressive art studio in mind. Studios facilitating the creative practices of fantastic artists that we discuss depend on the support of their local communities in the form of both patronage and charitable giving. These invaluable programs depend largely on Medicaid funding and now more than ever rely directly on you as continued government support is increasingly uncertain.
Of course these studios are also places to find incredible holiday gifts. Visiting and collecting works of art that you love to live with is a powerful way to integrate disability (disparate thinking) into your life in a personal and authentic way. If there’s a progressive art studio in your community, you'll almost certainly find some of the most original and remarkably affordable local art is being created there. Alternatively, you can now purchase many artists’ work online, such as Sarah Malpass at NIAD, Evelyn Reyes at Creativity Explored, or Larry Pearsall of DAC on Amazon. Please refer to our side-bar directory for all studio locations and websites.
If you’re interested in supporting larger organizations that advocate for disability rights on a national scale, this year we offer the following two recommendations:
ADAPT has always been at the forefront of the fight for disability rights even before the ADA. These heroes have been putting their lives and liberty on the line all year to defend Medicaid, crowding the halls of Congress, crashing meetings, and staging sit-ins at the offices of our political leaders - getting arrested and accruing legal fees in the process. ADAPT is still a relatively small organization, but these individuals saved America this year and they need your support.
ADAPT protester Lonnie Smith arrested at a sit-in at Denver US Senator Cory Gardner's office opposing GOP health care bill cuts to Medicaid (Jon Leyba/The Denver Post via AP)
The ACLU, co-founded by Helen Keller, has always understood disability rights in their most progressive form to be essential civil rights. They have been providing the legal muscle behind this movement at crucial moments - some you may have heard of and others you may not. When the state of Oklahoma sent letters to Medicaid recipients in early November indicating their home care services would be terminated at the end of the month, an ACLU lawsuit sent the state legislature back to work.
Helen Rae at White Columns
Helen Rae, one of the progressive art studio movement's rising stars, currently has recent work on view at White Columns in NYC, marking her first east coast solo exhibition. Rae is quickly emerging as an important figure in this movement; her work is striking, wildly popular, and at 78 years old, her practice is one of great dynamism and momentum.
Read MoreStorytellers: Sara Malpass
We first encountered Sara Malpass’ work at NIAD in her solo exhibition What Are Words For, and have included her work in our latest curatorial project Storytellers, currently on view at LAND in Brooklyn. Selections by Malpass are featured in this exhibition in order to highlight the important perspective she offers in the discussion of narrative...
Read MoreEvelyn Reyes: Ritual, Rules, and Abstraction
San Francisco-based artist Evelyn Reyes has been diligently creating robust series of minimalist drawings at Creativity Explored for the past 15 years; over this time she has consistently maintained a presence in the contemporary outsider art discourse...
Read MoreA Conversation with Sophia Cosmadopoulos
Cosmadopoulos is currently a coordinator and facilitator at LAND Studio and Gallery, a progressive art studio provided by the League Education & Treatment Center in DUMBO, Brooklyn. Her valuable perspective is also informed by an uncommonly dynamic career in this field...
Read MoreGateway Arts
Gateway Arts, in Brookline, Massachusetts (just outside of Boston) is one of the largest and, arguably, the oldest progressive art studio in the country, originally founded in 1973 (just prior to the 1974 creation of Creative Growth by Katz in Oakland). Whereas the Katz west coast programs closely resembled the model we consider most progressive for a fine arts program from their inception, Gateway grew into this model over time and continues to do so. Today Gateway is an exicting and important program, home studio to many great arstis including Roger Swike (who was included in “Mapping Fictions” at The Good Luck Gallery), Joe Howe (recently noticed by Matthew Higgs for a potential solo show at White Columns) Yasmine Arshad, Michael Oliveira and many, many, others. The studio currently provides workspace and facilitation to over 100 artists.
Gateway was initially founded in direct response to a deinstitutionalization initiative (then named “Gateway Crafts”) as a weaving and ceramics studio for 10 individuals. Over the past 43 years, the program has grown, evolved, and maintained an effort to stay in touch with progressive ideas. A detailed history of Gateway and their relationship to the emerging progressive art studio movement is detailed in the essay “Outsider Art: the Studio Art Movement and Gateway Arts” by Rae Edelson, who has been the program’s director since 1978.
Yasmin Arshad, Untitled, marker on paper, image courtesy Gateway Arts
Gateway’s rich history is evidenced in their exceptionally dynamic approach to every aspect of what they do - the populations they support, the kind of art created, and methods they implement to promote and sell artists’ work. Even as they participate in fine art exhibitions at high level galleries, craft continues to be an important part of their program in a way that may be somewhat subversive to traditional ideas of fine art. More effectively than any other progressive art studio in the country, Gateway sells handmade craft objects in their own retail store, while also supporting the professional fine art careers of several of their artists.
The studio (a space they have been using since 1980) is separated into several sections, each of which is lead by a staff facilitator; artists rotate among the various work spaces from day to day on a regular schedule. This approach is conducive to (or strongly encourages) artists to work in a wide range of media. This isn’t uncommon, many studios have workspaces for various uses, usually based on media (ceramics, printmaking, sculpture, etc.). Gateway has an exceptionally large number of spaces, providing a wider range of ideas, which have come into being over a long period of time and aren’t necessarily defined by media in the typical sense.
Gateway’s main studio includes workspaces for “Pottery”, “Folk art”, “Fabric”, “Paper, “Weaving”, and “Art Making”; in addition to the main studio, “Studio A” provides various creative supports and resources for those with psychiatric disabilities. Each area has a supervisor/facilitator who specializes in its respective media and each artist has a weekly schedule that determines which area they work in daily. A potential problem with this complex structure is that it could distract from an artist’s ability to develop a consistent, independent method of working within any one medium. An artist like Roger Swike, however, demonstrates that Gateway leaves room for artists with a well developed vision to operate independently from this structure when they’re prepared to do so. While Roger may sometimes dabble in other media if he chooses to, he’s free to engage with his own practice of working on paper, that he has developed over the course of his long career with Gateway.
Learning to understand the unlimited potential value of a work of art is an important aspect of being an artist, and an important concept for progressive art studios to endeavor to communicate to their artists. Intuitively, one might imagine that the creation of lower value craft objects in the same space as fine art may undermine the studio’s ability to communicate that concept (and uphold that principle). For many programs, the fine art standard is considered to be directly in conflict with craft for this exact reason. Craft in Gateway’s studio, however, is rooted in a tradition of understanding craft as art on a higher level. Artistic director, Steven De Fronzo explains that during Gateway’s formative years in the 80s, the creative community in the Boston area embraced craft as an alternative to an art world that felt inaccessible, or elitist. In this way, craft was akin to the outsiderism of the time.
The fine art vs craft conundrum has a complicated history in progressive art studios; at its most problematic, craft programs are designed and operated on the assumption that individuals with disabilities aren’t capable of making fine art. In these cases, the studios can become assembly workshops that produce crafty “handmade” objects. In their best form, however, providing resources in a progressive art studio to engage in craft diversifies the opportunities available to artists in a way that is essential. Programs that don’t have an admissions process based on a portfolio review inevitably have many artists who will find craft processes and creativity with functional ends as a more intuitive or appropriate path.
In practice, what's most essential is how the artist chooses one path over the other, and how the standard is maintained - creative projects of any kind are created with as much independence and creative freedom as possible. As the the art world progresses, new facilitators bring new ideas to Gateway - as the use of craft processes becomes more prevalent in contemporary art, the use of craft processes become available in their studio on those terms. Staff facilitators present concepts about art-making in terms of their own expertise; ultimately at any progressive art studio, the onus is on artists to staff as examples, not authorities, with artists making choices about their approach to art independently. The critical element is that this relationship is understood by the staff, and independence or divergence from the structure is encouraged when it begins to emerge.
Mapping Fictions: Daniel Green
Daniel Green, Fifteen People, 2009, Mixed media on wood, 14.25 x 22.5 x 1.75 inches
Daniel Green, Little Mac vs Soda Poponski, 2015, mixed media on wood, 11.5 x 15 inches
Daniel Green, The Sun, 2015, mixed media on wood, 6 x 16.5 x 1 inch
Daniel Green, Business Delivery, 2011, Mixed media on wood, 13 x 29 x 1 inches
Daniel Green's process is slow and intimate; quietly hunched over his works in the bustling studio, he draws and writes at a measured pace. These detailed works are an uninhibited visual index of Green’s hand; when read carefully, they become jarring and curious, slowly leading the viewer to meaning amid the initial incoherence. Green’s text is poetic and complex - language and thought translated densely from memory in ink, sharpie, and colored pencil on robust panels of wood. Figures and their embellishments are drawn without a hierarchy in terms of space occupied on the surface; they are at times elaborate and at other times profoundly simple. The iconic figures’ facial expressions (Jesus, Abraham Lincoln, Tina Turner, video game characters, etc.) are generally flat with proportions stretching and distorting subject to Green’s intention.
Ultimately, these drawings compel the viewer to internalize and decipher Green’s ongoing, non-linear narrative. His drawings call to mind Deb Sokolow’s humorous, text-driven work, but are less diagrammatic and concerned with the viewer. In an interview with Bad at Sports’ Richard Holland, Sokolow elaborates on her process:
I’ve been reading Thomas Pynchon and Joseph Heller lately and thinking about how in their narratives, certain characters and organizations and locations are continuously mentioned in at least the full first half of the book (in Pynchon’s case, it’s hundreds of pages) without there being a full understanding or context given to these elements until much later in the story. And by that later point, everything seems to fall into place and with a feeling of epic-ness. It’s like that television drama everyone you know has watched, and they tell you snippets about it but you don’t really understand what it is they’re talking about, but by the time you finally watch it, everything about it feels familiar but also epic. (Bad At Sports)
Much like Sokolow, Green engages in making work that begins with the rigorous practice of archiving information culled from his surroundings and interests, which then develops into intriguing, fictitious digressions. Dates and times, tv schedules, athletes, historical figures, and various pop culture references flow through networks of association - “KURT RUSSEL GRAHAM RUSSEL RUSSEL CROWE RUSSEL HITCHCOCK AIR SUPPLY ALL OUT OF LOVE…” Although the listing within his work sometimes gives the impression of being intuitive streams of consciousness, most of it proves to be very structured and complex within Green’s system. Rather than expression or even communication, the priority seems to be the collection of information or organization of ideas; the physical encoding of incorporeal information as marks on a surface is a method for making it tangible, possessable, and manageable.
Daniel Green, Pure Russia, 2011, Mixed media on wood, 9 x 23 x 3.5 inches
Pure Russia (detail)
From the perspective that Green invents, there’s an endless number of time sequences that haven’t been considered before. A grid of days and times (as in Pure Russia) imagines time passing in increments of one day and several minutes, then returns to the beginning of the series, stepping forward one hour, and proceeding again just as before. It could be cryptic if you choose to imagine these times having a relationship to one another, or it could instead be an original rhythm whose tempo spans days, so that it can only be understood conceptually as an ordered structure mapped through time - the significance of the pattern superseding that of specific moments.
By blurring the distinction between the articulation of ideas through text and the development of mark-making, Green’s highly original objects become unexpectedly minimal and material, yet simultaneously personal and expressive.
Daniel Green’s work will be included in Mapping Fictions, an upcoming group exhibition opening July 9th at The Good Luck Gallery in LA, curated by Disparate Minds writers Andreana Donahue and Tim Ortiz. Green has exhibited previously in Days of Our Lives at Creativity Explored (2015), Create, a traveling exhibition curated by Lawrence Rinder and Matthew Higgs that originated at University of California Berkeley Art Museum and Pacific Film Archive (2013), Exhibition #4 at The Museum of Everything in London (2011), This Will Never Work at Southern Exposure in San Francisco, and Faces at Jack Fischer Gallery in San Francisco.
Courttney Cooper
Cincinnati Map, 2010, ballpoint pen on collaged paper, 64" x 88"
Untitled, 2015, ballpoint pen on collaged paper, 52" x 80"
Cincinnati Map, 2009, ballpoint pen on collaged paper, 51" x 85"
Cincinnati Map, 2009 (detail)
Cincinnati Map, 2009 (detail)
images courtesy Western Exhibitions and Visionaries + Voices
Cooper’s oeuvre is a ongoing narrative featuring Cincinnati, imparted with adoration and idealism. Drawings that are tenaciously committed to archiving the city’s developing reality in bic ballpoint pen, Cooper documents the destruction of old buildings and construction of new ones, while modifying details to reflect the time of year (often after they've been hung in an exhibition space). But they are also richly populated with celebratory, idealistic imagery - flags flying on rooftops, hot air balloons traversing the sky above the river, “Do not be afraid, be a precious friend! Zmile, you’re in Zinzinnati Ohio USA 2011”.
Cooper’s works are often characterized as maps, which isn’t an entirely accurate categorization. Visionaries + Voices’ Krista Gregory points out:
I've come to learn that Courttney has been drawing "aerial views" of Cincinnati since he was a small child, first using an etch-a-sketch. His mark-making certainly reflects having this type of information/tool...I see the work that Courttney creates more in the vein of landscape, or townscape; as they are romantic in their visceral love for this place...I think that this work being categorized as ‘maps’ is misleading and couches them in something that is more related to Courttney's disability rather than to what it is that he is actually expressing and creating. They are not accurate. They are not drawn completely from memory. I've witnessed people hold on to wanting to think these things because it makes the work accessible or novel in some way. I sort of think that it is a reductive way to see them
The desire to see Cooper’s works as maps may be the consequence of trying to categorize autistic thinking - relegating autistic artists as spectacles of savant-ism. Courttney Cooper, however, is not comparable to Stephen Wiltshire, for example; his drawings are not an accurate configuration of streets as a road map indicates, nor are they a repetitious anonymous depiction of a city in an illustrative way. They're indeed informed by an intimate experience with his city - an astounding wealth of information accumulating across increasingly massive surfaces (created by gluing together scrap paper that Cooper gathers while working at Kroger). But this isn't the subject of the work, it's only the formal foundation that serves as a vehicle for Cooper’s voice. Cooper’s drawings are a complex and authentic network of specific places and structures; his streets are composed of details from memory or observation, cataloging expressions of particular perceptions in particular moments. The relationship of these moments to each other in space is approximated, as in memory - all of which culminates in a dizzying realm of overlapping information that becomes a living record, adorned generously with nostalgic, commemorative expressions of community and identity.
Zinzinnati Ohio USA: The Maps of Courttney Cooper curated by Matt Arient, is a selection of Cooper's drawings from 2005 - 2015, currently on view at Intuit through May 29th. Cooper is represented by Western Exhibitions in Chicago, where he has an upcoming solo exhibition November 12 - December 31, 2016. Cooper has maintained a studio practice at Visionaries + Voices in Cincinnati since 2004; he has exhibited extensively in the greater Cincinnati area and has work in the Cincinnati Art Museum collection. Selected exhibitions include the Wynn Newhouse Exhibition at Palitz Gallery, Syracuse University (as a 2015 Wynn Newhouse Award recipient), Cincinnati Everyday at the Cincinnati Art Museum, Maps + Legends: The Art of Robert Bolubasz and Courttney Cooper at Visonaries + Voices, Studio Visions at the Kentucky Museum of Art, Cincinnati USA: Before Meets After at PAC Gallery, and Indirect Observation at Western Exhibitions.
Sylvia Fragoso
Untitled, glazed ceramic
Untitled, glazed ceramic, 14" x 7" x 7", 2013
Untitled, glazed ceramic, 17" x 11" x 11", 2015
Untitled, glazed ceramic, 15" x 8" x 5", 2014
all images courtesy NIAD
Sylvia Fragoso’s methodically hand-built sculptures are crafted with a deceptive indelicacy and thick layering of glazes - small monuments in which form is defined by seeking rather than devising. Much like the ceramic work of Sterling Ruby or Julia Haft Candell, Fragoso reaches a compromise between concept and process. Where opportunities arise, she inserts symbolism that declares an identity for the work; subjects common in her drawings such as church and family are translated into physical form in a manner analogous to the way that her method of building with clusters of shapes on paper translates to her process of building with clay. References to function or representation are ultimately denied in favor of material manipulation and aesthetic - a revelation of the joy of making.
In a recent Art In America article The Happy Medium, Leah Ollman discusses the re-emergence of ceramics in the contemporary art discourse (especially in L.A.):
A new shift, roughly a decade old, has been catalyzed not by a single or even a few strong personalities, but by a broader redefinition and realignment of creative practice. Increasingly post-disciplinary, artists roam freely among mediums, unencumbered by traditional boundaries and hierarchical divisions. Many show a renewed interest in work of the hand, which they see as an antidote to theory- and concept-driven art. A messy physicality is often their (defiant) answer to the disembodied digital; theirs is a rising constituency for authenticity which advocates the material over the virtual.
This shift has extended to progressive art studios as well; in addition to Fragoso, other self-taught artists creating exceptional ceramic work are Mirov Menefee of The Canvas in Juneau, Alan Constable and Chris Mason of Arts Project Australia in Victoria, Cameron Morgan of Project Ability in Glasgow, Tanisha Warren at Creative Growth in Oakland, and Billy White, also of NIAD.
Fragoso (b. 1962) has exhibited recently in Hold Onto Your Structure : The Ceramics of Sylvia Fragoso at NIAD Art Center (2016), Telling It Slant organized by Courtney Eldridge at the Richmond Art Center (2015), Visions et Créations Dissidents at Musée de la Création Franche in Bégles, France (2014), ArtPad SF at the Phoenix Hotel in San Francisco (2013), and extensively in group exhibitions at NIAD, where she has maintained studio practice for many years.
Untitled, graphite on paper, 24" x 18"
Deveron Richard
Sectra Shower, watercolor on paper, 18" x 24”, 2014
The Milkets, watercolor on paper, 26" x 32”, 2015
The Planets, watercolor on paper, 17.25" x 23.5”, 2009
A Border Between Unicorns, watercolor on paper, 19" x 25.5”, 1996
Deveron Richard maintains a creative practice at one of many ECF art centers in the LA area (previously discussed by Disparate Minds in terms of their relationship to DAC Gallery). His inaugural solo show is currently on view in LA at the Good Luck Gallery through May 21st. From the Good Luck Gallery:
“An idiosyncratic iconography of visionary space travel and anthropomorphic sexuality arrives via the South Bay of Los Angeles through the singularly fertile imagination of Deveron Richard. Winged horses in brassieres and high heels glide peacefully around the cloud-enshrouded towers of a futuristic city, polar bears in lipstick and slit dresses prance through a fluorescent arctic landscape, and provocatively-attired unicorns face off on a hallucinatory geometric color grid. These hybrid creatures of exaggerated femininity exude a quirky eroticism. Rendered in watercolor with a distinctively saturated palette, inventive draftsmanship and hypnotic backdrops of complex rhythmic patterning. Other works depict interplanetary battles with rockets hurtling through galaxies and deadly beams shooting into space.”
Marvin Asino
From the Disparate Minds collection: “For all of my friends and one basketball player” is a zine containing 21 poems interpreted from the text works of Marvin Viloria Ariza Asino. It’s sensibility can be described using Marvin’s own words “rhythm; kind, beautiful, friendly.” Asino writes in a matter-of-fact manner (siding in a space where humor and simple, profound truths meet), so the force of its beauty comes entirely by surprise with a wonderful sense of mystery.
This anthology was given in the course of a conversation with one of Marvin’s many friends, Robert Grey, at Full Life, in Portland Oregon last year. An updated overview of Full Life, a very different kind of program, will be posted soon.
Billy White
My Body, mixed media on canvas, 18" x 24", 2015
Jed Clampett, glazed ceramic, 10" x 7" x 4"
Untitled, acrylic, 18" x 24", 2015
Untitled, graphite on paper, 12" x 17"
Untitled, mixed media on canvas, 24" x 18"
The process of evaluating any artwork includes some interpretation of how it functions - mechanisms such as the way gestural brushstrokes communicate movement by indexing the physical action of their application, or the way that arrangements of representational imagery can imply relationships between elements that generate narrative.
The mechanism by which Billy White’s paintings elicit emotion is sharply specific, yet escapes analysis, remaining a wonderful mystery. A loose, fearless application of paint renders forms with a striking physicality and sense of humor. There’s an uncanny affinity with the work of figurative painters Todd Bienvenu and Katherine Bradford (who both have an aesthetic undoubtedly informed by the work of self-taught artists). The impact of White’s work cuts through a vivid alternate world that operates on White’s terms - a highly original set of priorities, passing over image and rendering to achieve an expression of mood and vitality, as though excavating the underlying stories that were already present; impatient mark-making and barely legible imagery find time and space for redolent storytelling and detail. While he typically focuses on painting and drawing, White occasionally creates small ceramic sculptures that are rich in character and evocative of Allison Schulnik’s warped clay figures - slumped postures, elongated, rubbery appendages, intermingling glazes, and sunken, cartoonish expressions.
White’s work is largely influenced by his avid interest in pop culture, often depicting actual and imagined events in the lives of various celebrities or fictional characters, from Dr Dre to Hulk Hogan to Superman. NIAD provides some insight into White’s process: “He might start off painting Bill Cosby, but quickly change his mind by lunch. When that happens, he simply works right on top and doesn’t erase what came before. The new work becomes an extension of the old. By the end of the day this could happen several times and what’s often left is a latticework of figures and stories with interchangeable meanings.”
Billy White (b. 1962) has exhibited previously in Rollergate at the Seattle Art Fair, Telling It Slant organized by Courtney Eldridge at the Richmond Art Center, Undercover Geniuses organized by Jan Moore at the Petaluma Art Center, ArtPad San Francisco at the Phoenix Hotel, and extensively at NIAD Art Center, where he has maintained a studio practice since 1994. He has an upcoming solo exhibition at San Francisco’s Jack Fischer Gallery later this year.
The Effortless Humor of Michael Pellew
Michael Pellew, Untitled, 2016, Mixed Media on Paper, 11"x17"
Michael Pellew, Michael and Latoya Texting on the Beach, 2015, Acrylic on Canvas, 12"x9"
Michael Pellew, British Platter, 2015, Mixed Media on Paper, 14"x17"
One of the fantastic surprises at the Outsider Art Fair this year was our experience with the work of Michael Pellew. Pellew’s work is unassuming, and in the context of the fair particularly blends in - a style defined by repetition, drawing within a simple system, and the use of unconventional materials (markers). We were more familiar with his series of small original drawings marketed as greeting cards, which typically feature a grouping of four or five figures (available at Opening Ceremony in Manhattan and LA). In a larger scale, the voice only available in snippets in smaller works unfolds to become an astonishing comedic performance.
The repetition and economy of visual language in his work is necessary to the humor - each figure articulated in an identical manner, with just a few distinctive features describing its specific identity. The supreme ease with which each character enters the scene via this agile visual vernacular accounts for the works’ pace and timing. There's an exciting cleverness in the way the simple archetype of the figure takes on the identity of countless celebrities, analogous to a skilled impressionist mimicking pop culture icons in rapid succession. Pellew seems to be compiling an ongoing, shifting catalog of celebrities; those with apparent relationships or categorizations are sporadically interrupted with unexpected pairings (Princess Diana and Lemmy Kilmister) or fictional personas (Lauryn Hill M.D. from Long Island College Hospital, The Phanton Lord). Viewers with an extensive knowledge of pop culture are highly rewarded by the ability to recognize the abundance and subtlety of his references.
Michael Pellew, Untitled, 2015, Mixed Media on Paper, 22"x30"
Humor is an important element in many works that don't necessarily make us laugh, but truly funny art like Pellew’s (beyond the occasional clever moment or inside joke), is very uncommon. Crystallizing the elusive and ephemeral quality of comedy into a permanent art object is extremely difficult to achieve. Usually the most overtly funny approach is to employ an explicit punchline that rests on an impressive technical or procedural spectacle; artists that exemplify this approach are those like Wayne White or Eric Yahnker.
Eric Yahnker, Beegeesus, 2005, 13 x 10 x 10 in.
"Bible whited-out except that which sequentially spells Bee Gees" image via www.ericyahnker.com
Pellew’s humor, however, is more nuanced, so in the absence of a punchline, his approach relies on absolute fluency rather than overt technical prowess. The quintessential example of this brand of humor is Raymond Pettibon; works that appear effortless afford the artist a more casual voice, equipped to cultivate a more dynamic interaction between the work and viewer. When it's less obvious that there's a joke present, the viewer tunes into a more acute examination of tone and timing in search of the artist's intention.
Raymond Pettibon, image via www.raypettibon.com
Whereas Pettibon uses this approach to insert sardonic or satirical moments of levity into his generally grim oeuvre, Pellew instead engages this sort of humor with a lighter and even silly sensibility; he creates an abundantly bright and positive space that is captivating. The conceptual foundation of his work becomes about treading the line between earnestly identifying as an artist, or slyly engaging in play-acting the role of an artist. Walton Ford has described using play-acting (as a scientific illustrator) in a similar way as an entry point into comedy. In Pellew’s case, the performance is broader, and in its execution more engrossing - guiding you through his alternate world, you're always uncertain if he’s serious, even as he crosses well over into the realm of absurdity.
Michael Pellew, Michael Jackson and Bubbles, 2014, Acrylic on Canvas, 14"x11"
In the affable universe he realizes, there’s virtuosity in the way moments of comedic surprise cut sharply through. The lingering experience of these pieces isn’t static, but a dreamlike memory of an event unfolding; line-ups of celebrities…everyone had a pepsi…they were all hanging out around a limousine eating McDonalds…and then Marilyn Manson is offering his famous burger and fries. It’s an alternate reality composed of familiar characters and Pellew is leading us along, introducing each of them, all in his voice - but really it's the viewer’s voice. You are left walking away amused, incredibly satisfied, but not entirely sure what has just happened.
Pellew has been working at LAND Gallery’s studio for over ten years and participated in numerous exhibitions in New York, including group shows at Christian Berst Art Brut and the MOMA. His work has been acquired by many reputable collectors, including Spike Lee, Sufjan Stevens, Citi Bank, JCrew and PAPER Magazine.
Michael Pellew, Making a Band (detail)
Masters and Emerging Artists at the Outsider Art Fair
Art Project Australia’s Julian Martin at Fleisher/Ollman
At the 24th annual Outsider Art Fair in New York, it was clear that there has been a profound shift. Superficially, the aesthetics are far from the folk art antique shop feel of the past, having assimilated to a presentation more typical of the mainstream - a change generally attributed to one of field’s most successful champions and current fair organizer, Andrew Edlin. On a deeper level, the definition of “outsider” is flexed to a degree that's able to contain a broad spectrum of idiosyncratic works - from the visionary scarecrows of the late Memphis-based artist Hawkins Bolden, to Marlon Mullen’s lush abstractions, to an installation of 3D printed sculptures designed by 65 unconnected collaborators (presented as the work of a manufacturing company, Babel curated by Leah Gordon). Abandoning category without losing identity, the context of this forum has evolved rapidly over the past few years.
In a review of the fair for Design Observer, John Foster recalls that at the inception of the genre, early outsider art dealer Sidney Janis introduced the concept that “serious art could be made by everyday people”, a notion that's difficult to sympathize with today (if artists aren't “everyday people” then what are they?). This train of thought still seems to have some novelty for some 74 years later, as illustrated by Barbara Hoffman’s odd New York Post headline “The artists at this amazing fair are prisoners, janitors, and mental patients”. Ultimately, Edlin has allowed the fair to begin to merge seamlessly with the mainstream by expanding to include a flexible set of principles rather than depending on this particular kind of romantic narrative structure. It’s no longer necessary that the artists work in isolation or live obscure, misunderstood lives.
Rather, it’s a space for excellent creative endeavors that are genuine and created for their own sake, or for a context not ordinarily included in the art world. The most essential principle underlying this movement is that the institution of the market isn’t what engenders great work. In a climate where Laura Poitras (a filmmaker and journalist with no prior fine art experience) has a significant exhibition opening today at the Whitney, the particular terms and intent with which the OAF brings divergent, highly original perspectives to the art world maintains a distinct and important purpose.
The beauty of this more elastic definition is its efficacy both presently and retroactively, indicating that this isn’t so much a shift in paradigm as a greater understanding of why these works have been so compelling all along.
Hawkins Bolden at Shrine
As usual, titans of the self-taught canon were featured extensively throughout the fair: Henry Darger, Joseph Yoakum, Adolf Wolfli, Jesse Howard, Bill Traylor, Thornton Dial, Minnie Evans, Martin Ramirez, Gayleen Aiken, Frank Jones, Royal Robertson, and James Castle, etc. These masters (the ones who have inspired so many to work in this field) continue to be represented by fantastic works, not due to a traditional romantic narrative, but because of genuine, sophisticated, and highly original visions, as evidenced by their conceptual harmony with work by contemporary “outsiders”.
The fair's strongest and most relevant exhibitions, however, were contemporary works by artists who maintain studio practices at progressive art studios - a dynamic collection of installations that were, in sum, a tour de force eliminating any question about their importance to this emerging sub-market, and potential to sustain, develop, and gain momentum.
Marlon Mullen at JTT/Adams and Ollman
Marlon Mullen, NEWS (P0329), acrylic on canvas, 24" x 36"
The fair’s most important moment, and starkest example of the flexed "outsider" categorization, was the joint exhibition of NIAD’s Marlon Mullen by New York’s JTT Gallery and Portland’s Adams and Ollman - a solo exhibition of reductive acrylic paintings, with content explicitly referencing the contemporary mainstream. The narrative justification for its inclusion would be the assumption that these abstractions are defined by an unusual way of thinking and seeing, as opposed to a neurotypical artist’s contrived deconstruction of found imagery. Whether Mullen is engaging in abstraction in the traditional sense, creating representationally from his own perspective, or whether there is no meaningful difference between representation and abstraction in his experience is impossible to determine. Ultimately, their genesis becomes irrelevant because the elusive power of the imagery is an amalgamation of the inherently expressive nature of the work's formal elements, which isn’t dependent on a mutually understood way of seeing. The real triumph and importance of Mullen’s work lies in the revelation that their mysterious conceptual origin only causes their success to be more fascinating, and that they’re pushed to a degree of technical sophistication that’s unmistakably impactful. His paintings are paradoxically thoughtful and casual, as awkward as they are bold, as messy as they are delicate. These pieces embody a deeply genuine and intuitive quality that coexists with a strength defined by specificity and fine tuning.
Helen Rae at The Good Luck Gallery
Helen Rae, July 1, 2015, colored pencil and graphite on paper, 24" x 18"
The fair’s most generous moment was The Good Luck Gallery’s installation of stunning Helen Rae drawings - surfaces saturated with vigorous mark-making culminate in robust, stylized worlds rendered in graphite and colored pencil. Rae’s counter-intuitive re-imagining of the boundaries between abstraction and representation are thrillingly confounding. Strong graphic or patterned passages have an inexplicable sense of depth and form, which transition into fields scattered with spare details, achieving an almost photographic quality - all of which emerges from a surface that (when examined closely) possesses a roughly inscribed physicality. The continuous stream of excellent new drawings replacing sold work served as a testament to the promise of this prolific septuagenarian as an emerging phenomenon to watch.
Andrew Hostick at Morgan Lehman
Photos do little to capture the true nature of Andrew Hostick's drawings at Morgan Lehman Gallery. Not evident above is the experience of approaching this simple red, blue, and brown figure eight to discover that it’s surrounded by an opaque, shimmering field of marks in white colored pencil, worked hard into the mat board surface. The mystery of choosing to color a white surface white, is in its own way explained and not compounded by its eventual effect: fantastic moments of wonder in a distinct and familiar space. The curious effect of this subtlety achieved in such a laborious manner lays a foundation for the elusive mood that runs throughout all of Hostick’s works. He seems to search for, and with great success, achieve abstractions that aren’t just poignant in a general sense, but evoke a beautifully bleak, arid quality that seems to romantically belong to Ohio.
Andrew Hostick, Leon Polk Smith: A Constellation with Works on Paper, graphite/colored pencil on mat board,
Kenya Hanley, Family Matters, 2015, Mixed Media on Paper, 17" x 14", image courtesy Land Gallery
Other highlights included the velvety pastel abstractions of Art Project Australia’s Julian Martin at Philadelphia’s Fleisher/Ollman, humorous, pop-culture driven drawings by Kenya Hanley and Michael Pellew at LAND Gallery, Harald Stoffers at Cavin Morris Gallery, Joe Minter and Lonnie Holley at James Fuentes, Evelyn Reyes, Daniel Green, and Camille Halvoet at Creativity Explored, Terri Bowden, Susan Janow, and William Scott at Creative Growth, Walter Mika and Victor Critescu at Pure Vision, and an impressive quantity of work by artists at Japanese studios. Although only 4 progressive art studios exhibited independently at this year’s fair, their respective artists were prominently featured in a quarter of the exhibitions, including those of the most prominent dealers.
Henry Darger and Judith Scott at Andrew Edlin
Susan Janow, Untitled, colored pencil and micron on paper
Harald Stoffers, Brief 164, March 10th, 2012, ink on paper, 39.25" x 27.5", image courtesy Cavin Morris Gallery
Lonnie Holley at James Fuentes, NY
One of the most important insights from this year's Outsider Art Fair is that the progressive art studio can no longer strive to position itself as a neutral, invisible player between self-taught artists and an outsider art gallery. Undeniably, progressive art studios are poised to be a truly important movement, but, reflecting on this changing landscape it’s important that they critically evaluate their role in presenting work to the market. Despite their prevalence at the fair, gallerists had no reservations about expressing that they’ve been forced to stop representing artists they believe in due to studios' failures, ranging from unethical behavior (such as gifting works to program board members) to providing intrusive facilitation to simply being disorganized. The process of translation from outsider to the mainstream fine art market is delicate, and is something outsider art dealers are just now learning to do effectively; they’ve been an asset to studios because of their willingness to represent unique artists without ties to the broader art community. As the distinction continues to break down between outsider and insider, however, studios can only continue to be relevant if they’re able to proactively take on the responsibilities of translation and promotion typically provided by gallerists (including handling and documenting artwork properly).
The future of this process is pioneered right now by career paths that resemble the ones profiled above: NIAD, JTT, Adams and Ollman, and Marlon Mullen; Visionaries + Voices, Andrew Hostick, and Morgan Lehman; First Street, Helen Rae, and Good Luck Gallery; and Creative Growth, William Scott, and White Columns. Progressive art studios must believe in and champion each of their great artists with respect for their individual vision, with a focus on developing careers that extend beyond their program of origin.
Mark Hogencamp, Untitled (IMG_2616), Digital C-print, 27" x 36", 2014
In the traditional narrative of outsider art, the career of an artist such as Mark Hogencamp would have ended with the initial discovery of Marwencol. Ideally in the past, he would have been deceased before the work was found and his fixed oeuvre would be intrinsically associated with the story of a strange man working in isolation and obscurity (much like Darger and Ramirez). Mark Hogancamp, however, is no longer obscure or working in isolation. His new work at this year's fair, scenes created using full-sized mannequins, are a clear and exciting new development in his creative process. Hogancamp’s work is not at all diminished by the open involvement of his facilitator and gallery director Eddie Mullins, who we spoke with at One Mile Gallery’s booth. In our conversation with Mullins, his relationship with Hogencamp was remarkably familiar. Marwencol is a project absolutely devised and driven by Hogencamp, but Mullins has no inhibitions about explaining that the use of mannequins began after he provided some for Mark. Mullins plays an instrumental role in how Hogencamp’s vision is ultimately seen as art, but his assistance isn’t mistaken for collaboration (much like the relationships sound engineers and producers have with musicians). In this way, the transparency of this relationship sets an important example for studios to follow.
Recognizing the true nature of the facilitated creative process, including that provided by artist staff in the studio, must be fully open to criticism in order to progress; it’s simply too personal, dynamic, and delicate to be left out of the discussion. The next wave of great artists will come out of progressive art studios that are not only assisting artists to initiate a creative practice, but also provide innovative and ambitious new facilitation methods to further develop dynamic bodies of work.
Mary Ann James
Heaven, graphite and watercolor on paper, 2015
Train, graphite, micron, and watercolor on paper, 2015
Camping, graphite, micron, and watercolor on paper, 2015
Untitled, graphite and watercolor on paper, 2015
Mary Ann refers to all of her works as her “creations”. Like a story teller, she’s inspired by a combination of personal experiences in her daily life and concepts that she values, such as motherhood and heaven. Consequently, her works have a narrative feel - depictions of people and places that may be part of a story.
Mary Ann’s process, however, is not guided by narrative, but rather by an ambition to create. As a result of this, her subjects aren’t rendered as two-dimensional images, but intended to exist in their own right, in a two-dimensional world. In effect, her imaginative nature inevitably imbues the world she creates with a narrative life, but this distinction in her creative practice is important. Because she's creating rather than depicting, a figure, for example, is drawn in its entirety before clothing is drawn onto it - often a layer of flesh tones is painted before a subsequent layer of paint is added for the color of their clothing. If she includes shoes or gloves for a figure, she draws them around the foot or around the hand, rather than over it. Figures standing in front of a train are placed below the train, rather than in front of it, because both the train and people are created separately. Mary Ann has a highly original way of translating her perception of reference images onto paper, often distorting the scale of objects and editing out details that don’t fit her vision.
In the world she creates, scale is an expressive choice; each form is given whatever space it needs to exist and relate to the world it occupies. Ultimately in her work, she creates people and things to stage a still, timeless moment that’s simple, complete, and good.
Mary Ann James maintains a studio practice at The Canvas, a progressive art studio in Juneau, Alaska.
Joe Zaldivar selected by High Desert Test Sites
A Joe Zaldivar drawing was selected for the High Desert Test Sites 2015-2016 Limited Edition Postcard Series. Zaldivar, a prolific artist who maintains a studio practice at First Street Gallery Art Center in Claremont, California, has created an extensive body of work using Google Maps Street View images as reference material; this particular piece depicts the Sky Village Swap Meet in Joshua Tree, where the HDTS headquarters is located. Proceeds from postcard sales support future HDTS programming, projects, and events. A few highlights of their compelling and diverse programming include Andrea Zittel's A-Z West, Noah Purifoy's Outdoor Desert Art Museum, and the Sky Village Swap Meet. Notable contemporary artists who have exhibited with HDTS include Allan McCollum, Lisi Raskin, Cayetano Ferrer, and Siebren Versteeg, among many others.
You can purchase one of Zaldivar's postcards here.
From High Desert Test Sites:
High Desert Test Sites is a non-profit organization that supports intimate and immersive experiences and exchanges between artists, critical thinkers, and general audiences – challenging all to expand their definition of art to take on new areas of relevancy.
As a conceptual entity we are dedicated to "learning from what we are not." We believe there are many ways to live, and that learning from others can offer new insight and perspectives on ourselves, and the everyday environments we may think we already know well. Our mission is inspired by those visionary individuals who have made their work their life practice – who create intellectually rigorous and culturally relevant work regardless of the market or other outside factors.
HDTS programs include guides to the high desert’s cultural test sites, immersive excursions, solo projects, workshops, publications, and residencies.
NEW VOICES
Throughout 2015, Disparate Minds writers Tim Ortiz and Andreana Donahue worked directly with The Canvas, a progressive art studio in Juneau, Alaska as Artists-In-Residence, guest facilitators, and curators of the group exhibition NEW VOICES.
Read MoreGrace Coenraad
Grace Coenraad, Untitled, micron, sharpie, graphite, and india ink on paper, 2015, 16" x 16"
Grace Coenraad, Untitled, micron, sharpie, and india ink on paper, 2015, 22" x 22"
When I first painted a number of canvases grey all over (about eight years ago), I did so because I did not know what to paint, or what there might be to paint: so wretched a start could lead to nothing meaningful. As time went on, however, I observed differences of quality among the grey surfaces – and also that these betrayed nothing of the destructive motivation that lay behind them. The pictures began to teach me. By generalizing a personal dilemma, they resolved it.
Gerhard Richter, From a letter to Edy de Wilde, 23 February 1975
Coenraad’s dark, minimalist works are the product of a measured and slow process, executed with extreme diligence. Using 08 black microns, traditional pen and ink nibs, and occassionally graphite, she densely hatches careful lines, which slowly collect on the surface over many hours of work. This method is a clear path leading to an absolute resolution - the surface being obscured by black. The magic of these pieces (although they’re inextricable from the story of the steadfast execution of this simple method) lies in content that’s fantastically nuanced and complex. The black square is a subtle, jagged field comprised of various sheens and tones - certain patches are tinted by an initial application of bright watercolor (often pink or blue) that has bled through the subsequent, inevitable layer of black. The marks made using microns are incised, and those created with india ink and nib lift the paper slightly away from the surface, resulting in a textured surface reminiscent of Richard Serra’s black oil stick drawings. And much like the reductive, sublime paintings of Richter or Clyfford Still, Coenraad demonstrates that the honest act of mark-making isn’t reduced when it’s stripped of intentions or illusion. Conversely, it only becomes more revealing and mysterious.
After his first museum exhibition of entirely black drawings in 2011, Richard Serra was described by critic Roberta Smith as hermetic, abstract, difficult, and austere, an assessment that he accepted, describing it as “a virtue.” Explaining that art has to be difficult, Serra said that drawing independent of the flamboyance of color interaction, mark-making on its own, in black on white, proves to necessitate invention, thereby providing a “subtext” for how an artist thinks. For him, allover black works were a move to escape that convention of drawing as a “form to ground problem” to create works concerning “interval and space” rather than image.*
Coenraad didn’t stumble upon this principle inadvertently like Richter; for her, it’s a process that reflects a way of being. It is, as Serra articulates, an extension of the thought process and more. To a degree that’s rarely seen for non-performative artists, Coenraad is an artist for whom the boundary between life and art is blurred. Every task is executed with the same resolute sensibility, engaging life with a singular and sophisticated method in pursuit of perfection. Every bite of food is carefully selected and examined before being eaten (ingredients of an undesirable color rejected), every mundane task is afforded great consideration. For years she has worked part-time at a document destruction facility, where no one has been able to compel her to obliterate more than one document at a time. At home, blackening crossword puzzle squares for hours with ballpoint pen or sharpie is part of her daily ritual.
In the studio, Grace is fully immersed in her practice - working with her face close to the surface, she becomes absent from anything exterior of the drawing process. Occasionally she will stop and look around the room for a moment like a deep sea diver rising briefly to the surface, before submerging again. Grace doesn’t discuss her work, not because she can’t, but because there seems to be nothing necessary to say once a piece is finished.
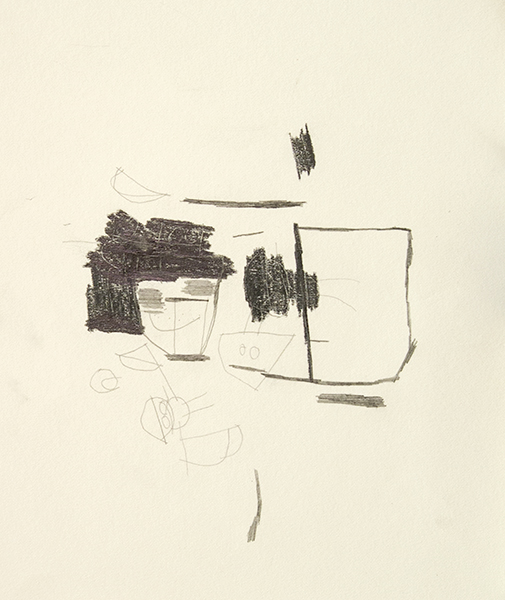

Between her larger, long-term works, Coenraad sometimes creates small graphite sketches, thoughtful experiments that serve as a point of entry into her mysterious thought process. The placement of faces demonstrate the dynamics of orientation in her drawings. The coexistence of elements in combination with turning the paper many times while working isn’t incidental to the process, but essential to it.
Coenraad is a Juneau-based artist who maintains a studio practice at The Canvas in Juneau, Alaska. Her work will be included in an upcoming group exhibition curated by Disparate Minds writers Tim Ortiz and Andreana Donahue at The Canvas' exhibition space in December.
Progressive Practices: The Basics
We’ve added a new section on the site for pieces of writing concerning the methodology of progressive art studios. We hope these will be a valuable resource to those involved in this work, as well as anyone interested in this emerging model for artist development. This piece, which discusses the basic, essential components of a progressive art studio, is the first of many. As always, your feedback is appreciated.
installation view of Judith Scott - Bound and Unbound, a recent exhibition at the Brooklyn Art Museum
“...there was an extraordinary amount of very strong and wonderful work coming out of these three studios…These centers, all three of which had been founded by the same couple, Florence and Elias Katz in the 1970s and 80s based on the same principles…I started to become intrigued by the question of why was there so much wonderful work coming out of these three art centers and was there something they had in common, some kind of methodology that was bringing forth such wonderful art…the methodology which was proposed by Florence and Elias Katz...which had to do with giving adult artists with developmental disabilities an opportunity to work in communal studios at hours which reflected the common work hours, five days a week 9-5, that these centers be connected to the art world, that there be a gallery connected to the studio, that there be not teachers but facilitators who would assist the artists in making their work, and that there would be a sales element.
It’s interesting that the first of these centers was created at
exactly the same moment of Roger Cardinal’s famous Outsider Art definition of
outsider artists being cut off from the world and these centers were radically
connected to the world...”
- Lawrence Rinder, Director of the Berkeley Art Museum and Pacific Film Archive, discussing the exhibition Create, which he co-curated with White Columns’ Matthew Higgs in 2011. You can view the full panel discussion “Insider Art: Recent Curatorial Approaches to Self-Taught Art” here
The Create exhibition in 2011 was inspired by the observation that the three Bay Area Katz-founded progressive art studios (Creative Growth, Creativity Explored, and NIAD) have been consistently creating high quality works and using a similar methodology, but without having much contact with each other (or studios elsewhere in the country) since their establishment. Our own research has found that this phenomenon isn’t limited to the Bay Area; studios have emerged across the country since deinstitutionalization began in the 70s - programs where incredible, valid art is created and whose methods include the same basic points. Although many progressive art studios have referred to the Bay Area programs as a development model, most were created prior to any knowledge of them.
The spontaneous, isolated development of progressive art studios throughout the world indicates something important and unique about what these programs are and what they mean. The insight to be gained is that a model of acceptance rather than assimilation is viable and incredibly valuable, if the culture is forward-thinking enough to accept it.
Whereas an assimilation methodology depends on developing a way of working with a person experiencing developmental disabilities that successfully produces the prescribed result (using contrived means to alter a way of being or behavior, to fit given expectations), the acceptance methodology begins with a perceived potential and conforms expectations to meet that potential with an open-ended concept of success. The acceptance model appears spontaneously because the potential identified, the creative person, exists universally. Conversely, the desired outcomes of assimilation methods depend on esoteric “best practices” informed by idealized or archaic concepts of behavior, professionalism, or generally appropriate ways of being.
Marlon Mullen, an exhibition currently on view at Atlanta Contemporary
As Lawrence Rinder points out, for the acceptance methodology of a progressive art studio to emerge and excel, it must simply operate on a handful of fundamental principles:
A radical connection to the world
Rinder references a radical connection, in direct contrast with Roger Cardinal’s definition of Outsider Art which is dependent on artists creating in isolation. A progressive art studio is also radically connected to the world in contrast with traditional services for people with developmental disabilities.
Offering integrated services has long been an ambition of service providers for this population. This is not only because of the proven efficacy of integration, as demonstrated by examples of integrated schools, but also for the sake of cultivating a more inclusive community. In adult life, (post-school) the concept of integration and inclusion is far more complex; everyday life can not be simply “mainstreamed” the way that a school is. Progressive art studios provide opportunities for powerful forms of integration and inclusion that aren’t possible in any other form of support. Successful fine artists such as Judith Scott, Dan Miller, and Marlon Mullen (all of whom have been supported by progressive art studios) are the first examples of people receiving supported employment services who are internationally competitive and influential in their field.
This radical connection depends on the involvement of those at every level of the program who are personally invested in the practice of art-making. The work of facilitators and management must be informed by their knowledge of and personal investment in art (in the context of contemporary international and local culture, as well as art history). Employing fine artists as facilitators and studio managers also allows a connection to develop on a more fundamental level, in the peer relationships between artists in the studio (abstract of being on the providing or receiving end of services). This, in conjunction with the exhibition of artwork, offers unprecedented visibility and presence in the community, culminating in the best possible conditions for the development of genuine professional and personal relationships with other artists who are not paid supports.
Nicole Appel, Animal Eyes and Russian Boxes, colored pencil on paper, 19″ x 24″, 2014, Pure Vision Arts, NYC
Investment of time
Artists having access to the studio and utilizing it for periods similar to regular work hours is extremely important. This point is a matter of principle and a good vehicle for advocacy of the progressive art studio model as a whole.
Often, those involved in making decisions by committee with or on behalf of a person with a developmental disability (including parents, case workers, service coordinators, counselors, and other members of the “support team” who are not artists) will oppose large investments of time in the art studio. This occurs for the same reasons that parents oppose children pursuing artistic careers, schools persistently cut art programs, or illustrators, designers, etc. must argue the details of invoices with clients. Creative work as a valuable professional discipline is stigmatized as frivolous throughout american culture, and pushing for higher investments of time is the front line on which these studios combat this stigma. Although it takes place in a congregated and specialized setting, the progressive art studio is much like a job coaching service for those pursuing serious careers as fine artists.
Schedules should range from 6-8 hours per day and 2-5 days per week depending on how developed the artist is, what other employment services or opportunities they’re engaged in, and how much time they want or need to spend working on art. Generally speaking, artists should be permitted to commit as much time as they want to art-making and should be encouraged to commit as much time as they’re able.
Project Onward's studio space in Chicago
An open studio
The studio must be a space belonging to the artists that’s conducive to creative work, where artists gather to maintain studio practices (not unlike a group of like-minded individuals in any workplace). The concept of the artists owning the space is crucial; providing opportunities for people experiencing developmental disabilities to create art is far more common than actual studios are, and this idea is one of the key distinctions of an approach that’s truly progressive.
There’s an obvious, superficial transition that can be made from a traditional day habilitation program to a shared art studio space. Both are fairly open workspaces where individuals exert themselves productively; several existing studios were once day hab programs or still operate under the pretense of being so in the eyes of Medicaid. However, even if a day hab program shifts its focus completely to art-making and physically becomes an art studio, it’s not a progressive art studio until it achieves a complete conceptual shift of paradigm. The space must be one in which the artists are free to invent and strive to meet expectations of their own devising, not a space where they’re guided to meet the expectations of staff. Any intensive one-on-one, step-by-step directions, or didactic practices must be eliminated. The goal of a progressive art studio is not to provide therapy, education, or any influence of assimilation - it’s to validate an artist’s experience and foster the capacity to share that experience on their own terms.
It’s not necessarily the case, however, that a progressive art studio completely lacks an educational element. For studios that don’t have a limited admission with portfolio review, there’s a large group of new artists working in the studio who benefit from significant initial guidance in order to discover art-making and learn to value it. Also, the studio may need to set boundaries regarding the use of shared materials and it’s important all people using the space conduct themselves in a professional manner respectful of a communal work environment. This should be achieved with guidance and assistance as needed. Ultimately, though, the core goal must always be total creative independence.
installation view at DAC Gallery in LA
A gallery and sales element
The gallery and sales element of the progressive art studio provides at least two essential functions. Firstly, as discussed above, exhibitions of artwork are a powerful form of integration into the community that’s not available by any other means. Even in cases where the artists don’t share a physical work space with other artists who aren’t paid supports, their presence and visibility in the community through a gallery show fosters connections with other artists and the general public on the artist’s terms.
Secondly, the handling and display of the work in a fine art exhibition space allows the studio to set an important example in the community for valuing the ideas and experiences of those living with developmental disabilities. By handling and installing the work professionally and making a meaningful investment of space and time in the gallery, the program makes a profound statement about the value of the artist, their ideas, and voice.
Conversely, handling the work in a manner divergent from accepted standards of a professional artist, ie. overcrowded salon style shows, improperly installed or framed work, or uncritical exhibition of unsuccessful/unresolved works, makes the opposite statement about the work and artists, effectively presenting the work as other and lesser. Allen Terrell, Director of the ECF art centers and affiliated DAC gallery (one of the most professional gallery spaces directly affiliated with a progressive art studio) is driven by a simple principle: don't do anything with the artists’ work that you wouldn't do with your own.



